Harvesting insights through participatory process process, Brussels (2016)
Science, policy and practice interfaces for enabling innovation & sustainability
Harvesting insights through participatory process process, Brussels (2016)


This paper is the result of my travel to the policy studies. It is part a main part of my PhD research study and the PICK ME project but it also takes lessons learnt on governance and innovation policy during my research stays in Enschede and Manchester. The objective of this paper is to understand to what extent instruments designed at different levels of policy domains can be coordinated as part of an organic process. At the same time, it also tries to highlight some aspects of the story behind the emergence of the Spanish wind energy sector, a successful trajectory in terms of both energy and specialized technology production.
Davide and Elvira are my co-authors but also memorable fellows on this trip to policy studies.
 The launch event “Opening the development agenda,” the STEPS center – Sustainable Alternatives for Latin America, was held on 5 and 6 November in Buenos Aires. STEPS Latin America is part of a network of universities based China, USA, Kenya, India, the UK and Sweden. STEPS Latin America seeks to renew and open innovation agenda and sustainability of the region, based on the idea that there are different paths to development. During the two-day panel on Open Science, Innovation inclusive, horizontal innovations for sustainability and natural resources and development which will have important guests were made internationally. My participation in this event was to design and facilitation of participatory workshops with the aim of thinking policies to promote open knowledge production and think a new research agenda on innovation and sustainable development for the region.
The launch event “Opening the development agenda,” the STEPS center – Sustainable Alternatives for Latin America, was held on 5 and 6 November in Buenos Aires. STEPS Latin America is part of a network of universities based China, USA, Kenya, India, the UK and Sweden. STEPS Latin America seeks to renew and open innovation agenda and sustainability of the region, based on the idea that there are different paths to development. During the two-day panel on Open Science, Innovation inclusive, horizontal innovations for sustainability and natural resources and development which will have important guests were made internationally. My participation in this event was to design and facilitation of participatory workshops with the aim of thinking policies to promote open knowledge production and think a new research agenda on innovation and sustainable development for the region.
The workshop Policies to open the generation of knowledge was based in participatory techniques aimed to allow jointly identification of a number of items such as tools, methodologies and priorities related to S & T policy. Brainstorming techniques and World Cafe are used to enhance the diversity of perspectives and facilitate the exchange of ideas between different actors. The outcome of this workshop will be digitized and shared with participants to encourage collaboration in different areas.
The workshop Research agenda for sustainable development was based in participatory techniques for making maps on areas of knowledge and research priorities through a prospective approach. By visualizing a future scenario, the exercise seeks to help participants to relate different elements at different levels and over time in order to facilitate change processes at the system level. The outcome of this workshop will be digitized and shared with participants to encourage collaboration in different areas.
The event was part of the new line of collaboration between Transition Hub – Climate KIC and the STEPs center. Further actions are related with the co-development of learning materials and exploring research opportunities in the area of resilient and smart agricultural systems
See full agenda of the event here & summary of event in STEP website
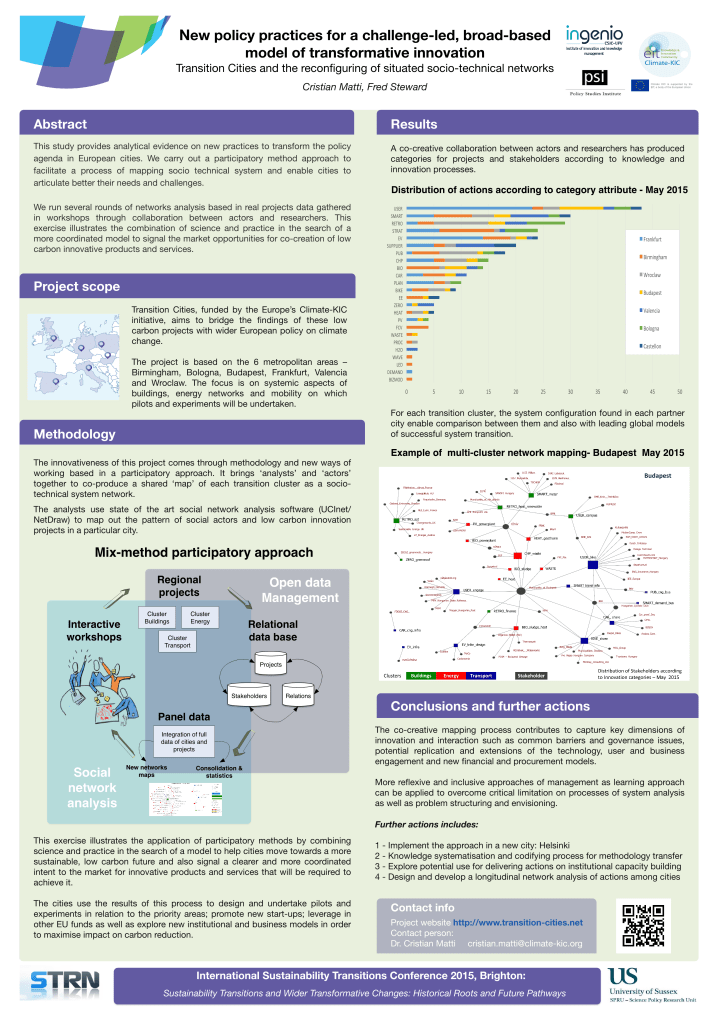
Transition Cities project (2015) and the reconfiguring of situated socio-technical networks
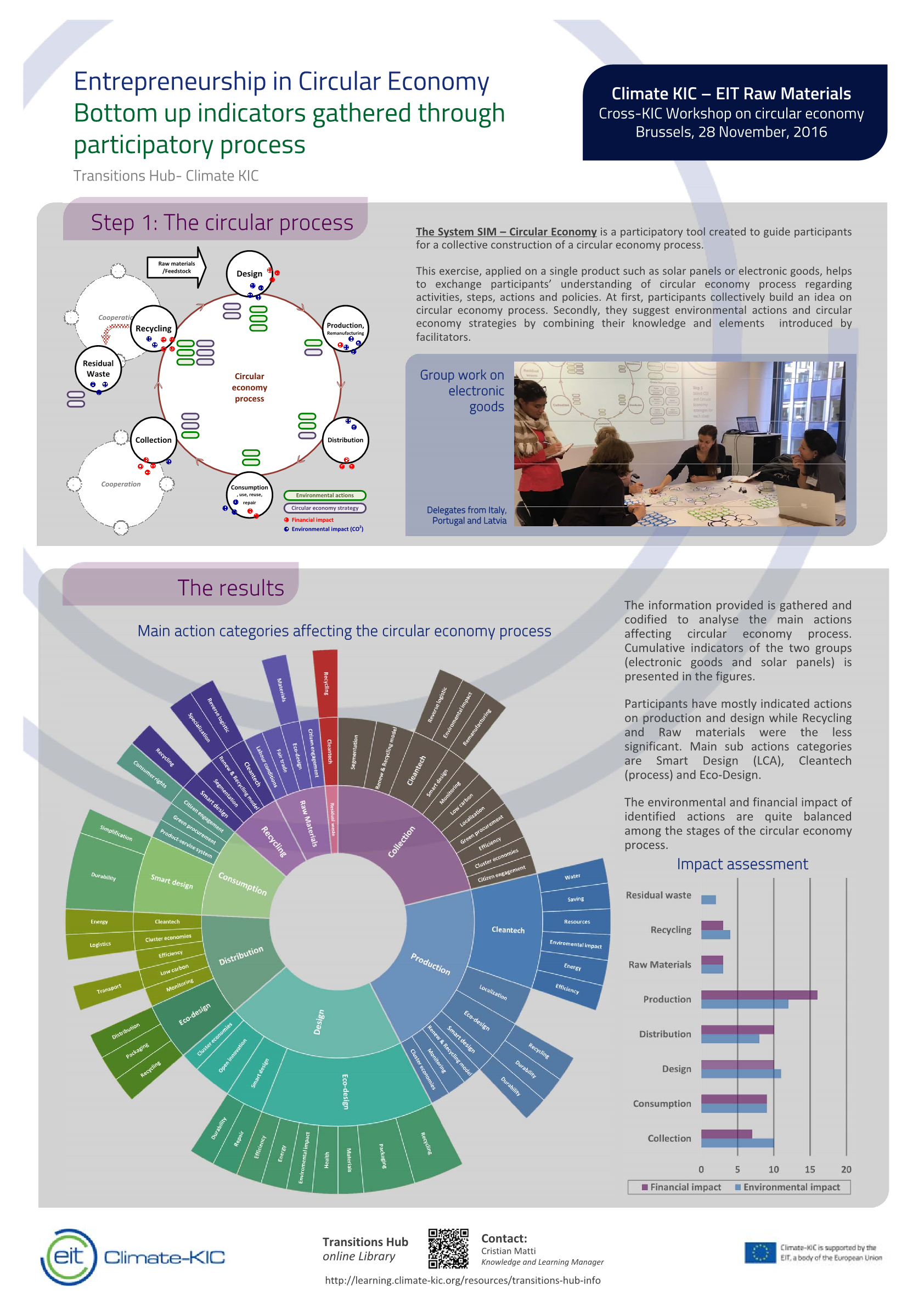
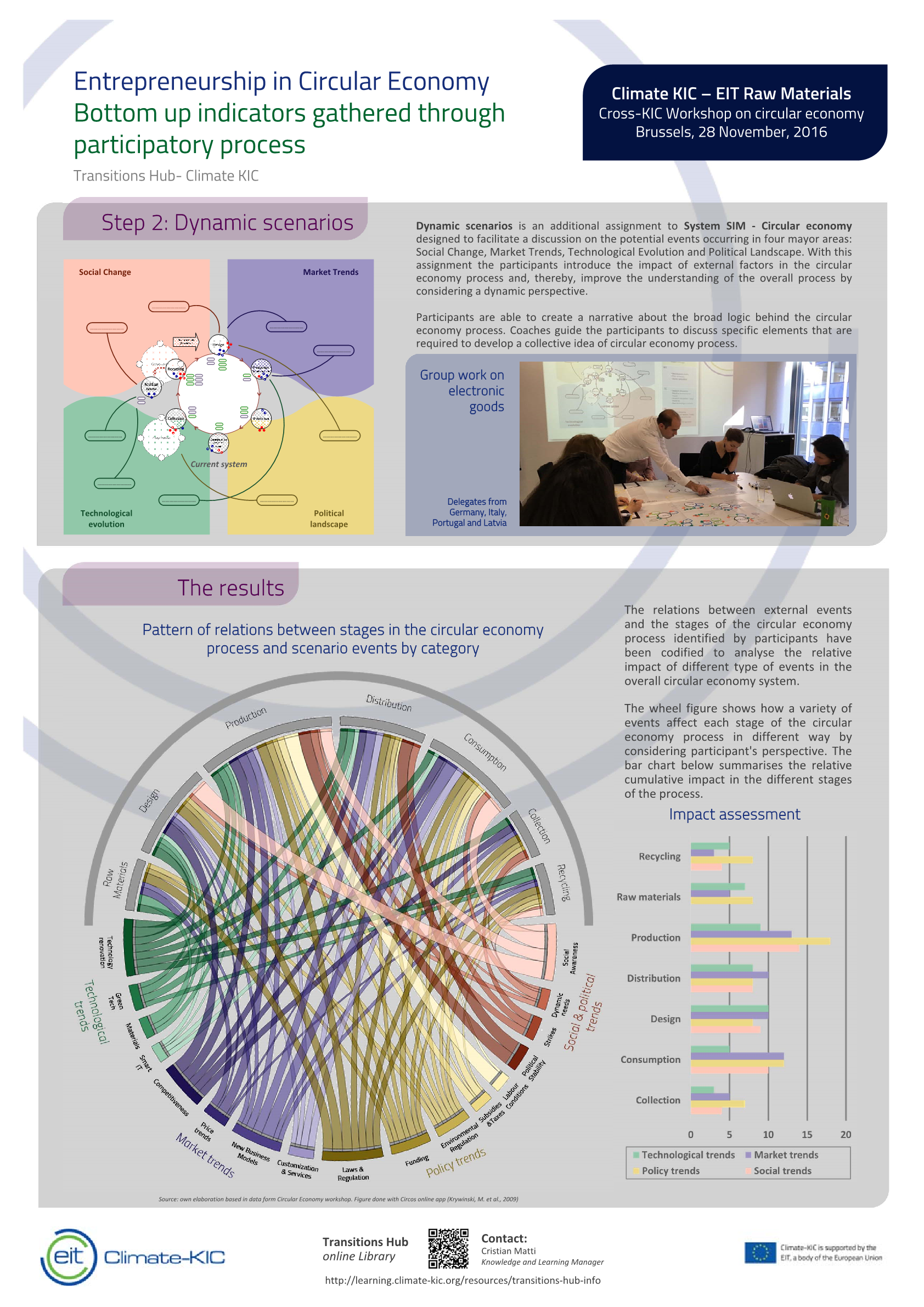
This study provides analytical evidence on new practices to transform the policy agenda in European cities. We carry out a participatory method approach to facilitate a process of mapping socio technical system and enable cities to articulate better their needs and challenges.
We run several rounds of networks analysis based in real projects data gathered in workshops through collaboration between actors and researchers. This exercise illustrates the combination of science and practice in the search of a more coordinated model to signal the market opportunities for co‐creation of low carbon innovative products and services.
Cristian Matti & Davide Consoli
The European Community (EC) has proactively promoted the development of renewable energy for over 20 years by means of standards and regulation designed to align incentives and opportunities. These actions have spurred a variety of responses and modes of implementation with distinctively local characters among member states. The diffusion of wind energy in Spain is a good case in point to illustrate how coordinated multi-level environmental policy can successfully promote the emergence of new sectors. Building on a wide platform of supranational and national directives, Spanish regional governments have designed and implemented development strategies based on the mobilization of locally available assets. This has resulted in differential growth of industrial, research and policy capacities across regions, and a rich spectrum of development trajectories that leverage on and feed back into regional-specific tangible and intangible assets. This chapter outlines the intertwining of technological, industrial and institutional developments that allowed Spain to become an active pole of innovation and growth in the wind energy sector.
Book: The Economics of Knowledge, Innovation and Systemic Technology Policy
Javier de Vicente López, Cristian Matti and José Jiménez Pérez
This document summaries the results obtained as a result of the participatory process that is part of the “Foundations for a Provincial Strategy Biomass” in the province of Castellon.
These actions are ultimately aimed at laying the foundations for sustainable biomass strategy, which included the set of actors in the territory and the entire value chain that the use of biomass genera.La idea behind all the participatory process It is incorporating the different viewpoints, knowledge and experience of all actors in the work of treating biomass as “an element to assess forest biomass” capable of “generating economic wealth, clean energy and employment, especially in the interior villages helping the development of these rural areas. ”
Download report here: Report Biomass Castellon – Participatory methods 2015 (in Spanish)
My DPhil research project analyses the long term pathways of knowledge creation within and across a multilevel environmental governance system. Emphasis will be put in the strategies for pursuing energy security of supply and for supporting renewable industry in Spain by considering areas of technology development and environmental policy through networks articulation.
The study focuses on mechanism for knowledge creation as part of government and industry response to the current multilevel framework on energy and environment. In doing so, this research seeks to identify the major contributors to the emergent knowledge base, be they individuals, research organizations, governmental agencies or firms. Finally, it will analyze the reasons behind differences in performance among Spanish regions.
This research will try to identify key environmental policy and technology factors that contributed to the development of wind energy sector in Spain. Emphasis will be put in the implementation pattern of policy instruments that facilitated pathways to develop renewables energy regionally as well as the extent to which the recombination of existing knowledge and new forms of organization within and across the value chain affected emergent technological capacity.
Theoretically, the research seeks to contribute to the understanding of the development of an emergence sector among a multilevel governance context but putting particular emphasis on interaction and interdependences within and across areas of technical development and environmental policy. It also aims to get a better understanding of processes of adaptation and integration of polices (emanating from higher hierarchical levels) to local context as a strategic response to face new challenges and opportunities.
PhD dissertation available HERE
The ongoing global economic crisis is seriously challenging advanced capitalistic economies. In the last year the GDP has fallen at dramatic rates, creating the conditions for the upsurge of unemployment, above all in areas characterized by specialization in mature industries. According to recent growth models and empirical evidence, innovation and knowledge creation represent the main factors able to improve the competitiveness and the long run perspectives of growth of countries. Yet, innovation and technology policies have mainly been designed by relying on a supply side perspective so as to affect the creation of knowledge by providing funds to carry out R&D activities and by enhancing education and training for researchers. However, a debate has recently emerged, about the need for grafting innovation and technology policies in a demand-oriented framework.
The aim of this project is to provide an original contribution to the ongoing debate, advancing the understanding of the mechanisms through which demand-based innovation policies may stimulate effective knowledge creation process, and eventually trigger competitiveness and productivity growth. To this purpose, the research activity will consist of both theoretical models and empirical analyses, the results of which should be able to inform the policy design process. We shall distinguish between public and private demand for both final and intermediate goods and services and will analyze their effects on the generation, diffusion and exploitation of technological knowledge by articulating the research activity on different dimensions (regional, sectoral and institutional). The research activity will be conducted by pursuing a great deal of multidisciplinarity and combining a number of diverse methodologies. The results of the analyses will in turn provide the basis upon which a taxonomy of demand-oriented technology policies may be elaborated.
Last and not least, my Dphil research project was the main input of the proposal for the study on Spanish wind energy sector included in PICK ME. Thus, the resulted project has provided an excellent academic environment to explore, validate and improve my research project.
Scientific outputs
Multi-level governance, policy mixes and wind energy in Spain